Socket Server Reference
This topic provides a summary of related documentation for the ESock APIs.
Socket Server APIs:
| Server session APIs | Header | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
ES_SOCK.H |
RSocketServ establishes and reserves resources for the base communication session to the socket server. All other client interfaces require a valid session to be opened |
RSocketServ Subsession APIs |
|||
ES_SOCK.H |
End point for all socket-based communications. |
||
ES_SOCK.H |
Makes host name resolution queries. |
||
ES_SOCK.H |
Used to startup and manage active connections. It is possible to start a connection either implicitly, via the RSocket or RHostResolver APIs, or explicitly via the RConnection API. The RConnection creates a default subconnection. |
||
ES_SOCK.H |
Used to organise channels within a connection and manage Quality of Service. Multihoming-aware applications must use this API. Only valid in the context of an RConnection. |
||
ES_SOCK.H |
Interface for network database access. |
||
ES_SOCK.H |
Provides an interface to resolve service names and ports. |
Bearer Mobility APIs
| Bearer mobility APIs | Header | Description |
|---|---|---|
es_mobility_apiext.h |
Comms Mobility API extension for application client running an Active Scheduler. |
|
es_mobility_apiext.h |
Comms Mobility API extension for application client not running an Active Scheduler. |
|
es_mobility_apiext.h |
Interface to be implemented by the application client to support mobility API extension. See Bearer Mobility Client. |
How APIs related to the 3-Plane Comms Architecture.
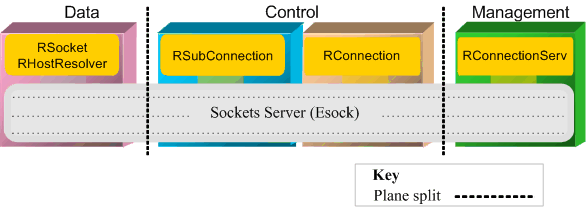
Figure: Figure 1 - How ESock APIs related to the 3-Plane Comms Architecture
The Sockets Client API also defines a number of support classes used in conjunction with the above interfaces. These encapsulate:
Addresses: a base address class
TSockAddris defined. Specific protocol address classes are derived from this. Each address can be identified by its Protocol Family, an integer which identifies protocol suites from others.Resolution queries: queries made through
RHostResolverobjects are packaged in TNameEntry descriptors. These are packages forTNameRecordobjects that containTSockAddrobjects to pass in addresses.Protocol information: a comprehensive description of a protocol’s capabilities and properties can be dynamically obtained through the
TProtocolDescclass. Capabilities are identified by constants.Endian issues: BigEndian, LittleEndian, and
ByteOrdercan be used to order integers to and from network order.
RSubConnection Events
CSubConGenEventDataClientJoined, CSubConGenEventDataClientLeft
These two events derive from CSubConGenEventDataClientBase, which provides the functionality for both. The source and destination
end points of the data client are presented with this event, along
with the IAP ID of the connection on which it was created.
CSubConNotificationEvent
Both generic and extension sub-connection events derive from this class. The rules for generic and extension events are the same as for parameter sets. That is, a generic event MUST be able to be understood by all technologies.
The IsGeneric() method identifies whether the
event is generic.
The GroupId() method returns
the UID of the factory that contains the event, and Id() returns the class type Id within that factory. These two pieces
of information comprise the STypeId of the event.
CSubConGenEventParamsGranted
Notification of
this event occurs after a request to SetParameters() has been made and negotiation with the network has been completed.
A notification will be received for each family contained in the parameter
bundle that was negotiated successfully. This event presents a generic
set and zero or more extension sets (providing they are supported
by the underlying sub-connection provider technology) of the parameter
family identified by the Id returned from GetFamily().
CSubConGenEventParamsRejected
Notification
of this event occurs after a request to SetParameters() has been made and negotiation with the network has failed for some
reason. It could be an error within the handset software/configuration,
or that the network could not provide the acceptable (minimum) level
of QoS. The reason for failure and the parameter family are presented
by the accessor methods Error() and FamilyId(). Like the CSubConGenEventParamsGranted event,
a notification for CSubConGenEventParamsRejected is received for each family in the parameter bundle that could not
be negotiated successfully.
CSubConGenEventParamsChanged
This event occurs when the properties of a parameter family
has been renegotiated due to some event on the network. It is not
sent in response to a request to change the properties. The change
could be the result of an error or just that the level of QoS has
improved/worsened. If a new set of parameters are available they’ll
be presented as with the CSubConGenEventParamsGranted event. The error status is presented via the Error() method.
CSubConGenEventSubConDown
This
event occurs when the underlying sub-connection has been lost. This
could be due to request for it to be closed, or some error on the
network. The error status is presented via the Error() method.
RSubConnection QoS Parameters
CSubConQosGenericParamSet
| Parameter | Description | Directions |
|---|---|---|
Bandwidth |
Bandwidth the client requires |
Uplink / Downlink |
Maximum Burst Size |
Maximum size of a burst of data the client can handle |
Uplink / Downlink |
Average Packet Size |
Average packet size required (e.g. codec use) |
Uplink / Downlink |
Maximum Packet Size |
Maximum packet size the client can handle |
Uplink / Downlink |
Delay |
Acceptable Delay/Latency |
Uplink / Downlink |
Delay Variation |
Acceptable variation in delay (also known as jitter) |
Uplink / Downlink |
Priority |
Relative priority the client expects to give this channel compared to it’s other channels |
Uplink / Downlink |
Header mode |
Specify whether the header size should be calculated by the QoS module or specified by the client. Default is to let the QoS module calculate it. |
N/A |
Name |
Identity of a “well known” set of QoS Parameters. |
N/A |
If an extension parameter set is added to the family that contains conceptually identical parameters to those in the generic set, it is recommended that you set both instances (generic and extension) of those parameters.
CSubConQosIPLinkR99ParamSet / CSubConQosR99ParamSet
Getter and setter methods are provided for each parameter.
Note: The constants used for it are KSubConIPParamsUid and KSubConQosIPLinkR99ParamsType.
The following parameter sets are available in Symbian platform.
CSubConQosR5ParamSet
It inherits from the release 4/99 set CSubConQosR99ParamSet. Although it is possible to add both this parameter set and the
R4/R99 one, it is not necessary and should not be done.
CSubConIMSExtParamSet
This class contains the IM CN Signalling Indicator flag.
Test programs
None