How to form links
This document describes how to use links within a doubly linked list.
To form a doubly linked list of CMyClass objects, include
the link object TDblQueLink as a component of CMyClass:
class CMyClass : public CBase
{
...
TDblQueLink iDlink;
...
};
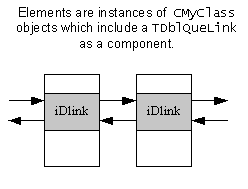
Although any kind of object can be an element of a linked list, most lists consist of elements which are all of the same type.
An object can participate in more than one list. For example, to allow CMyClass objects
to participate in two doubly linked lists, include two separate TDblQueLink objects
as components of CMyClass:
class CMyClass : public CBase
{
...
TDblQueLink iDlink1;
...
TDblQueLink iDlink2;
};
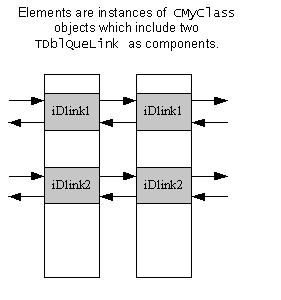
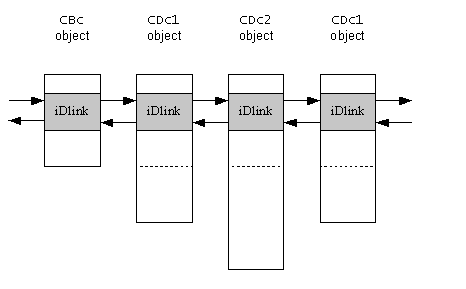
Elements can also be objects constructed from a variety of classes, all
ultimately derived from the same base class, where that base class includes
the link object as a component. For example, if CBc is a
base class for CD1 which, in turn, is a base class for CD2,
then the elements of the list can consist of a mix of CBc or CDc1 or CDc2 objects.
class CBc : public CBase
{
...
TDblQueLink iDlink;
...
};
class CDc1 : public CBclass
{
...
}
class CDc2 : public CDc1
{
...
}
New link elements are inserted into an existing list using either TDblQueLink::Enque() or TDblQueLink::AddBefore() function. Note that AddBefore() is not available in v5.
These are prototyped as:
void Enque(TDblQueLinkBase* aLink);
void AddBefore(TDblQueLinkBase* aLink);
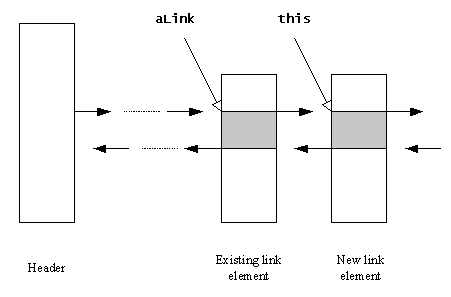
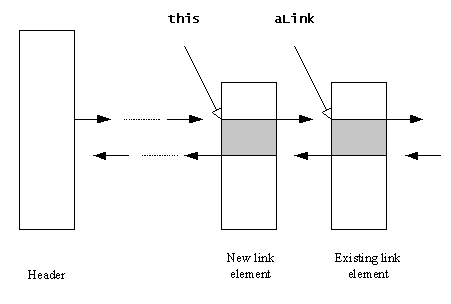
Calling Enque() on an element means that this element
is added to the list so that its position follows the element aLink,
as the following figure shows.
Calling AddBefore() on an element means that this element
is added to the list so that its position precedes the element aLink,
as the following figure shows.
Note that new elements cannot be inserted at the beginning or end of a
list using these functions. The AddFirst() and AddLast() members
of the header class TDblQue<class T> must be used
instead.