Array of variable length elements, flat buffer
Describes how elements of varying length are organised in the array buffer.
This is a CArrayVarFlat<class T> object whose
elements can have different lengths. Although each element is a class T object,
the length of that object can vary.
In this type of array, each element occupies its own individual cell allocated
from the heap. The array buffer contains fixed length data structures, one
for each element, which are physically contiguous within the flat array buffer.
Each fixed length data structure contains the length of an element (a TInt value)
and a pointer to it. The structure itself is part of the implementation but
occupies no more than eight bytes on 32-bit machines.
A flat buffer always occupies a single cell allocated from the heap and
is always extended by the process of reallocation. A flat array buffer is
implemented using a CBufFlat object.
The following diagram illustrates how elements are organised within the array buffer:
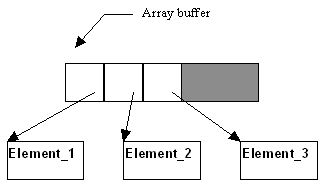
This kind of array is suitable for a small number of elements or for a moderately large but fixed maximum number of elements. It is not suitable for large arrays with a high turnover of elements.
This class is immediately derived from the abstract templated base class CArrayVar<class T> which
is itself derived from the abstract non-templated base class CArrayVarBase.