Libxml2 Overview
This section describes the libxml2 component which is a wrapper for the standard libxml2 C library.
Purpose
The libxml2 component provides XML processing, parsing and validation APIs. You can call its C functions directly or use the C++ wrapper.
Architecture
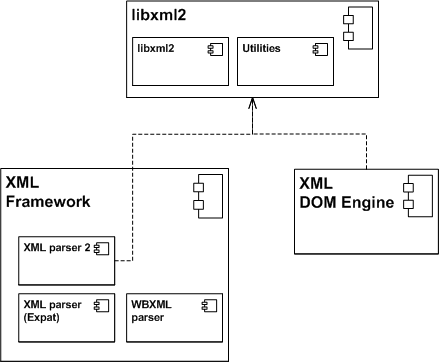
The libxml2 component is the core of the XML collection. Two other components rely on it: the XML Framework and the XML DOM Engine.
The libxml2 sub-component provides direct access to the C API of the standard libxml2 library.
The Utilities sub-component provides object-oriented access to the C functions: it also implements the resource management and error handling capabilities of the Symbian Platform.
If your Symbian Platform build does not include the libxml2 component, the XML DOM Engine and the libxml2 SAX parser plug-in are automatically excluded.
APIs
The XMLEngPushL() function opens and initializes the libxml2 library parser. The XMLEngPopAndClose() function closes the library parser and frees its resources. You must call the XMLEngPushL() function before any parsing and serialisation operations, and call the XMLEngPopAndClose() function when these operations are completed.
The following table lists the most relevant wrapper classes of the libxml2 library. High-level classes are in the XML DOM Engine component.
| API | Description |
|---|---|
Global data providing access to most of the libxml2 library: settings, function pointers, and so on. Available through TLS |
|
General-purpose string: pointer-sized object containing a zero-terminated UTF-8 string. |
|
Read-only version of TXmlEngString. |
The following table lists the most relevant C structures of the libxml2 library.
| API | Description |
|---|---|
Document. Provides access to the tree of nodes. |
|
Node. Provides access to its children and chain of attributes. |
|
Attribute. |
|
Element. |
|
Container for the contents of an element. |
|
_xmlSchema and _xmlDtd |
Validation trees. These structures have no C++ wrappers. |
XPath evaluation context. |
Typical uses
When porting existing software, use the C functions of the standard libxml2 library and refer to the libxml2 Reference Manual for more information.
To take advantage of the standard types and exception handling provided by the Symbian Platform, use the C++ APIs.