DBMS Overview
Provides an interface to relational databases.
Purpose
The DBMS component provides an interface to relational databases. It enables you to create and access databases either from a single client or from multiple clients sharing access over a server.
Required background
To use DBMS you need a knowledge of relational databases and the SQL query language.
Key concepts and terms
- Store database
A client-side single client database stored in permanent file stores, implemented by
RDbStoreDatabase- Named database
A database allowing simultaneous read/write access by multiple clients, implemented by
RDbNamedDatabase
Architecture
DBMS defines a general relational database access API, and allows different database implementations to be provided of which there are two: a small and relatively lightweight client-side implementation; and, for when multiple clients must have write access to a database, a client-server implementation.
When multiple clients can access the same database, transactions ensure that only one client can change data at a time.
The File Stores API defines a sophisticated file storage, called permanent file stores, that allows individual entries in a file to be modified. The database implementations use these stores for the underlying data storage.
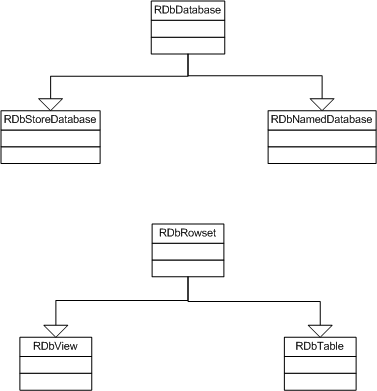
Figure: DBMS Class Diagrams
DBMS Summary
DBMS provides the following:
APIs
| API | Description |
|---|---|
Abstract database class. |
|
Implements |
|
Implements a named database. |
|
The base class for all rowset types. |
|
Provides access to table data as a rowset. |
|
Generates rowsets from an SQL query. |
|
A wrapper for an SQL string combined with a text comparison mode. |
|
Describes the desired shape of a view's pre-evaluation window. |
|
Provides notification of database changes to clients. |
Typical uses
DBMS is very well suited to applications with small to medium-sized datasets, where the total record count is less than 10,000 and the database size is less than 512KB. It scales reasonably well to larger datasets with total record counts less than 100,000 and database sizes less than 10MB.
DBMS is a suitable database engine for applications such as: