Location information
Location-based services (LBS) use coordinates from the World Geodetic System (WGS 84), which is also used as a reference system by the Global Positioning System (GPS).
The coordinates are based on values for latitude, longitude, and altitude (elevation above sea level).
The North Pole is 90 degrees North (+90 degrees) and the South Pole is 90 degrees South (-90 degrees). The Equator is defined as 0 degrees; locations above it have positive latitudes (0 to +90 degrees); those below (0 to -90 degrees) negative ones.
There are two definitions of North Pole; Magnetic North Pole and True (Geographical) North Pole. Any application with a compass must check how the API defines North Pole.
The Magnetic North Pole is the point to which compasses point. The True North Pole defines latitude as +90 degrees.
Meridians are constant longitudinal (north-south) values. The Prime (Greenwich) Meridian’s value is 0 degrees. WGS84, which LBS use, defines its zero meridian some 100 meters east of the Prime one. Locations east of the Prime Meridian have positive longitudinal values (0 to +180 degrees), those west (0 to -180 degrees) have negative ones.
As seen in the figure below, latitude lines are smaller near the poles. At the equator, one degree of longitude is roughly 111.3 km, whereas at 60 degrees of latitude one degree of longitude is only 55.8 km, which is more difficult to see.
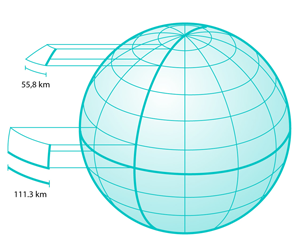
Figure: Length difference between latitude lines on the equator and at 60 degrees of latitude