Store Overview
Provides structured data storage, using networks of streams.
Purpose
It is often necessary to persist a data structure such as an object by writing it to memory as a sequence of bytes called a stream. A complex object is persisted as multiple streams collectively known as a store. The Store component provides access to stores in Symbian platform.
Required background
The Store component requires no specific background apart from C++ and Symbian platform.
Key concepts and terms
The API has the following key concepts.
- stream store
a store consisting of streams, implemented by
CStreamStore- persistent store
a store which persists beyond the lifetime of the application which creates it, implemented by
CPersistentStore- embedded store
a store which can itself be stored as a stream in another store, implemented by
CEmbeddedStore- memory store
a store which resides in memory and exists only for the life of the store object, implemented by
CBufStore- dictionary store base and streams
a sequence of streams accessed by a UID, implemented by
CDictionaryStore
Architecture
A stream is a representation of a data structure (such as an object) as a sequence of bytes. Structures as complex as most applications require multiple streams to store their state. This is termed a store. Stream types that work with stores are provided by the Store Streams API.
The Stores API defines both base classes that define store abstractions without specifying the storage medium, and some concrete store types.
The abstract classes are used as the base classes
of separate APIs which use particular storage media. In particular the File Stores API defines
further concrete stores which use file storage. Its base class, CFileStore extends CPersistentStore and
has its own subclasses such as CDirectFileStore. Concrete
store types do not have to provide all the stream manipulation functionality
defined by the base class interfaces: for example, direct file stores do not
support individual deletion of streams within a store.
Dictionary stores are accessed by a UID whereas stream stores are accessed by a stream ID. Persistent stores persist beyond the lifetime of the application that created them: they have a root stream from which the other streams in the store can be found. Embedded stores can be stored as streams in other stores: once written they cannot be modified.
Stores are integrated with the application architecture as defined in the Uikon Core API. That expects file-based and embedded applications to handle their data storage through stores.
Stores are also the basis of the relational database provided by DBMS.
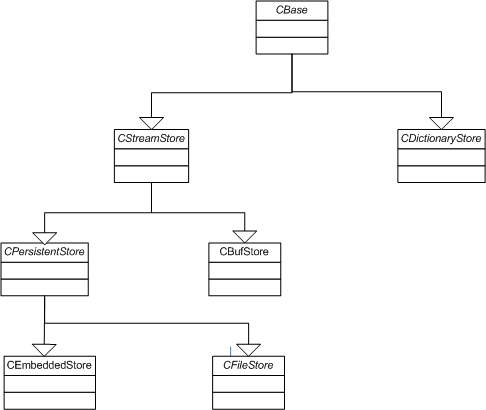
Figure: Store inheritance diagram
APIs
| API | Description |
|---|---|
Provides the core abstract framework for stores allowing streams to be created and manipulated |
|
Persistent store abstract base class |
|
Encapsulates an embedded store |
|
In-memory non-persistent store |
|
Dictionary store interface |
|
Supports the opening and manipulation of an existing stream in a store |
|
Supports the writing of a stream to a store |
|
A stream buffer hosted by a file |
Typical uses
A typical use of stores is to write files to memory without using the file server. This is a good thing to do when an application uses embedded documents.