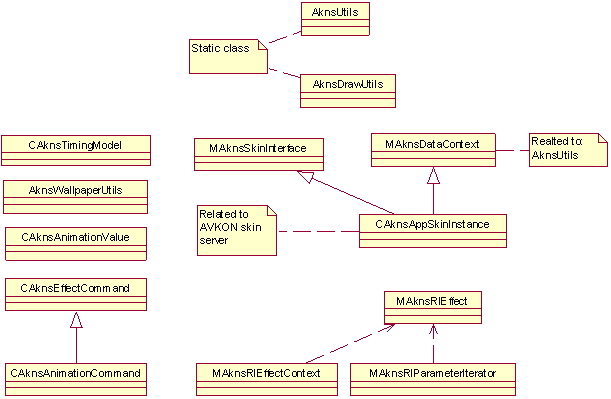
Figure 1: The class diagram of skin drawing, skin utility, and skin animation classes.
Skins API provides services for UI controls and applications. These services consist of:
To make a UI control (for example, one defined by the application itself) skin-aware, it may be necessary to modify its drawing code. For example, if a control clears its background, it must be done using a method provided by AVKON Skins.
To make a UI control use resources provided by the skins (for example, bitmaps), the control must be modified so that it retrieves the resources using AVKON Skins interfaces and reacts properly to the skin change event.
Any container that occupies the full main pane (or pop-up window) needs to be modified to provide a skin control context. This is done to specify how layout backgrounds are used by its child controls.
AVKON Skins also provides means to cache skin item data objects and to control the lifetime of a cached item data object. It is up to the application (or UI control), whether it will or will not take advantage of these.
Each skin item represents a single resource (i.e., bitmap or application icon) that can be retrieved using the AVKON Skins interfaces. A skin item is identified by its identifier.
Item identifiers are common among all skin packages. They are mapped to concrete resources (skin item data objects) using skin item definitions. Item definitions for system-wide skin items are stored and managed by Skins Server. Most applications and components have, however, no reason to do so.
Typically, a UI component needs to obtain or construct an item data object by providing the corresponding item ID to the AVKON Skins subsystem. An item data object (or a resource instance extracted from it) is returned to the caller.
Skins API supports only S60 skins. If application needs skinning of its own bitmaps, it has to implement skinning.
Provides utility methods to perform skin-aware drawing operations, such
as background drawing for a UI control. Contains the following class: AknsDrawUtils.
Supports AVKON Skins common operations. AknsUtils provides utility methods
to initialize skins support, retrieve a pointer to the current skin instance
or data context, and to perform other skin-related tasks. Contains the following
class: AknsUtils.
A utility class for manipulating the Idle state wallpaper. Contains the
following class: AknsWallpaperUtils.
In order to maintain binary compatibility and to avoid passing additional
parameters to child controls, skins support relies on context information
passed in the control hierarchy using the MObjectProvider mechanism.
An overview of the MObjectProvider functionality is provided
in Symbian Developer Library.
For example, when the Background() method of AknsDrawUtils is
called to draw the bitmapped layout background for the control, the object
provider chain is searched for a control context and the nearest one (i.e.,
the control context provided by the nearest parent) is used to specify the
bitmap and layout for drawing. This implies two requirements for controls
and applications:
The entity that provides the control context is usually the one that represents the layout element that defines the background to be used. For the status pane and control pane, the control context is provided by their implementation. For the main pane, the control context may be provided by the system classes (for instance, when an AVKON control covering the entire main pane is used), but in other cases should be provided by the application. The proper place for this is usually the container that occupies the main pane.
If no control context is found, the drawing operations provided by AVKON Skins function as the corresponding methods in Symbian OS UI Graphics Utilities. This ensures backwards compatibility with applications that are not aware of the skins support even if they use controls that take advantage of AVKON Skins.
Contains the following classes:
CAknsBasicBackgroundControlContextCAknsListBoxBackgroundControlContextCAknsLayeredBackgroundControlContextCAknsFrameBackgroundControlContextCAknsContainerDataContextThe skin instance takes care of updating cached item data objects when item definitions change and they are owned (and therefore deleted) by the skin instance. The caller is responsible for updating independent objects.
If the UI control can be drawn even when the skin instance singleton is
not available (for example, during an AppUi destroyer), it must handle situations
when skin support is not available and AknsUtils::SkinInstance returns NULL.
Every UI control should also be prepared for error conditions caused by skin
item retrieval and should handle leaves or NULL return values
properly.
Contains the following classes:
CAknsItemDataCAknsImageItemDataCAknsImageTableItemDataCAknsBitmapItemDataCAknsColorTableItemDataCAknsMaskedBitmapItemDataCAknsBmpAnimItemDataCAknsAnimationItemDataCAknsEffectQueueItemDataCAknsStringItemDataThe main use cases of Skins API are:
Skins API classes with their inheritance and composition relationships.

Figure 1: The class diagram of skin drawing, skin utility, and skin animation classes.
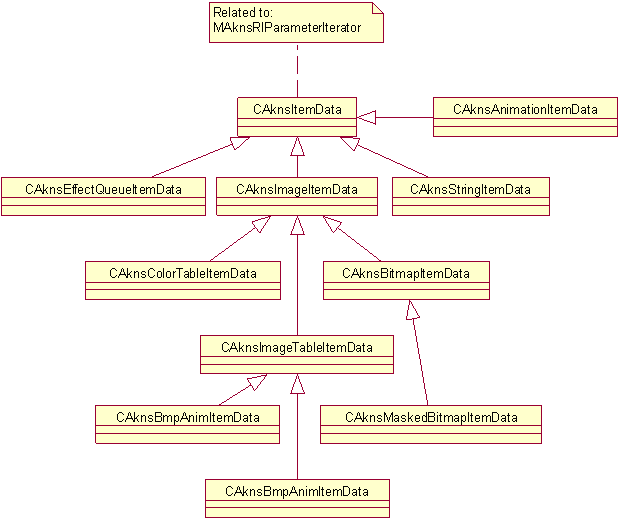
Figure 2: The class diagram of skin item data classes
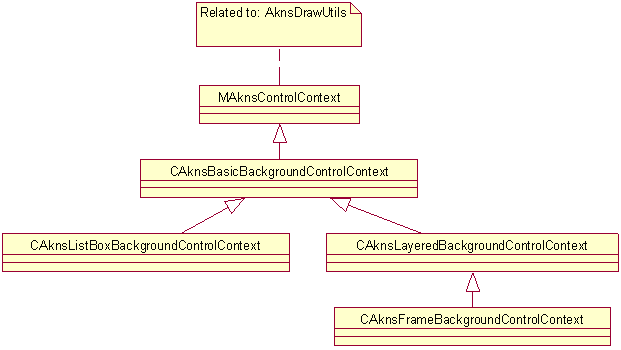
Figure 3: The class diagram of control context classes