CAG has been adapted for 2D from Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG). CSG is a modeling strategy for 3D that combines the half spaces formed by planes, spheres, toroids, and cylinders to form an arbitrary shape through boolean operations.
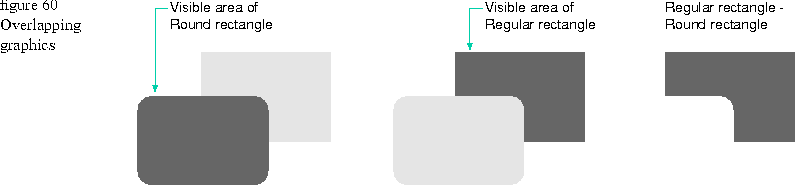
Areas are often used to define the clipping boundaries of graphics. For example, when one geometry overlaps another geometry, an area can subtract the top geometry from the underlying geometry to represent the remaining visible portion of the underlying geometry.
Figure 60
The idea of combining one geometry with another geometry to create an arbitrary shape has many applications. See the heading "Examples" on page 106 for other ways in which areas can be used.
[Contents]
[Previous]
[Next]
![]() Click the icon to mail questions or corrections about this material to Taligent personnel.
Click the icon to mail questions or corrections about this material to Taligent personnel.